Projects need materials, consumables, or assistance from external sources, and an RFQ is immensely helpful in such conditions.
This contractual manuscript conveys the buyer’s needs to potential dealers. They will examine the RFQ, seek clarification if needed, and provide their answers. The customer may also arrange a meeting for bidders to address any uncertainties they may have.
Explanation & Significance
RFQ proposes the buyer’s requirements to sellers, enabling them to study the prerequisites and submit their proposals containing pricing and other terms and conditions.
RFQ is also referred to as Invitation for Bid and is employed when the requirements are clearly determined. In RFQs, buyers can request cost quotes per commodity, hour or other units of height.
Different types
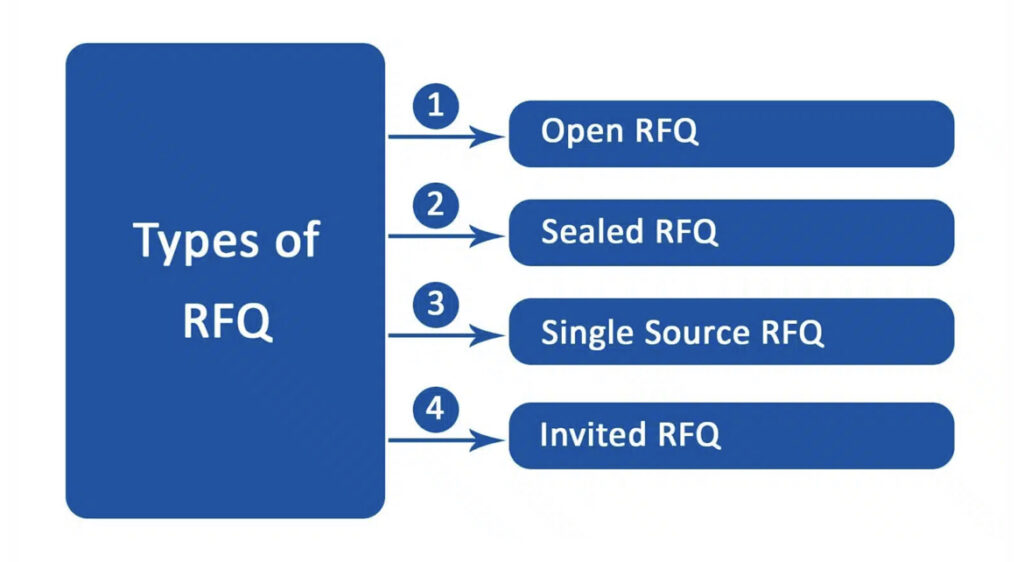
Open Request for Quotation (RFQ)
Up to the submission date, sellers in this form of RFQ are able to view and edit their bids. In turn, this encourages competition, which raises the buyer’s price. On occasion, though, it might result in price fixing due to seller collusion.
Sealed RFQ
In the public and government sectors, this RFQ is frequently utilized. The bids are sealed before the deadline and only opened then; the tender is available to all sellers. Though it might not always offer the greatest deal or allow for haggling, this RFQ ensures transparency.
Single Source RFQ
When purchasing spare parts from a specific manufacturer or authorized seller in the buyer’s territory, an RFQ is typically given. Bidding is only permitted from the manufacturer or their authorized representative. Despite the generally good material quality, costs are sometimes more than average because there is little to no competition.
Invited RFQ
To save time and get better work in this situation, the buyer invites bidders from a pre-selected list. By accelerating the process, this produces high-caliber work. Even though this approach saves time, it might not produce the greatest deal.
The Process
The bidding process is streamlined by a well-defined RFQ procedure that includes thorough requirements, terms and conditions, payment information, delivery guidelines, inspection standards, etc.
For outlining their criteria, the majority of companies have a template. This makes it easier for bids to present information in a systematic way so that buyers may quickly analyze the responses.
You can break down the RFQ process into five terms:
1. Prepare the RFQ Document
The initial step involves gathering requirements. It’s important to involve relevant stakeholders in this process.
An RFQ may include the following information:
- Technical specifications of materials;
- Carrier and delivery requirements;
- Terms for inspection and payment;
- Local regulations to be considered;
- Validity period of the quote;
- Quote prepared by;
- Quantity;
- Unit price;
- Total cost;
- Required skills;
- Competency levels and training requirements;
- Descriptions of parts;
- Contract duration;
- Terms and conditions;
- Delivery date;
- Discounts for bulk orders;
- And more.
2. Define the Vendor List
This step is optional. If you have a pre-selected list of vendors for specific items or services, you can specify them and exclude others from quoting.
3. Issue the RFQ
You can release the RFQ with a deadline for submissions once the specifications are specified and management approves. Ensure that all bidders receive answers to their questions by giving them enough time to prepare their bids and a way to ask for clarification. A bidder conference can also be advantageous.
4. Receive and Review Offers
Open the offers once the RFQ deadline has passed and evaluate their thoroughness. Accept the bids if they satisfy the specifications. After that, carry out a technical and commercial analysis.
5. Select and Award the Contract
Select the lowest offer that satisfies the technical requirements after the review. Choose the lowest offer after a few rounds of bargaining if it is allowed. Signing the purchase order creates a contract that is enforceable by law.
Why Do You Need RFQs?
They are valuable when it’s challenging to acquire the necessary materials or consumables independently, but they can be easily obtained through third parties.
- Additionally, RFQs are useful for procuring specific commodities, consumables, and supplies, where requirements are well-defined, and cost estimation is straightforward;
- During the project planning phase, RFQs are essential as they allow for a breakdown of tasks and estimation, scheduling, and monitoring to meet cost and timeline objectives;
- RFQs help fulfill requirements at an affordable rate and without complications, enabling the achievement of budgetary goals and project timelines.
Depending on the organizational structure, either the procurement manager or the project manager will be responsible for issuing the RFQ.
Using RFQs Effectively
In RFQs, sellers break down requirements into detailed elements for accurate cost estimation. Consequently, sellers may need to present their calculations as evidence to secure the contract.
- The buyer will assess the quotations and, once the contract is signed, will monitor project costs and progress throughout the project’s life cycle using tools like the Gantt chart;
- At times, suppliers may not fully comprehend the requirements, leading to unusually high or low price quotes, and they may overlook regulations and deadlines. It’s crucial to ensure their thorough understanding of all requirements before finalizing the contract.
Best Practices
- Suppliers should familiarize themselves with the terms and conditions before submitting their offers;
- Suppliers should quote prices based on prevailing market rates;
- During estimation, suppliers should consider the necessary skill sets for resources;
- Suppliers should utilize resource management data from previous similar projects as a reference;
- Suppliers should provide evidence of their technical expertise;
- Buyers should provide all necessary details in a well-organized format;
- Buyers should address any queries raised by suppliers.
Tools
Numerous project management tools available in the market offer capabilities.
Many open-source templates allow for the integration of RFQs into an organization’s PMIS tools, enabling buyers to access them instantly during the procurement process and visualize them using Gantt charts.
Compared to RFP
RFQ and Request for Proposal have distinct differences. In an RFP, the buyer presents a problem and seeks creative solutions from sellers. RFPs are commonly used for construction and service contracts, while RFQs are employed for procuring commodities. The RFQ concludes with a purchase order, whereas the RFP culminates in a contract.
In RFQs, pricing is the primary determining factor, whereas RFPs consider multiple factors such as pricing, technical expertise, experience, resource availability, legal requirements, and more, depending on the specific procurement contract.

Learn more
RFI stands for Request for Information, which is a non-binding document. Buyers issue an RFI to gather information from sellers, aiding in the development of the RFQ or RFP.
RFIs serve as communication tools, facilitating the exchange of information between buyers and sellers regarding products or services.
What does RFQ mean in project management?
RFQ, in project management, stands for Request for Quotation. It is a formal document issued by a buyer to solicit price quotes from potential sellers or vendors. The RFQ outlines the buyer’s requirements, including specifications, quantities, delivery terms, and other relevant details. It is commonly used when procuring commodities or materials. The RFQ allows the buyer to compare and evaluate different price quotes to select the most suitable supplier.
What is RFQ and RFP?
RFQ and RFP (Request for Proposal) are both procurement documents used in project management. While RFQ focuses on obtaining price quotes, RFP is broader in scope. RFP is used when the buyer has a problem or need and is seeking creative solutions from sellers. It typically includes detailed project requirements, evaluation criteria, and may involve multiple factors beyond just pricing, such as technical expertise, experience, and legal considerations.
What is the process of RFQ?
The RFQ process encompasses several steps. Initially, the RFQ document is prepared, outlining the buyer’s requirements. The optional step involves defining a vendor list. Following this, the RFQ is issued to potential suppliers, allowing them to submit their offers. Once the submission deadline is reached, the buyer proceeds to receive and review the received offers. After careful evaluation, the contract is awarded to the selected supplier who best meets the buyer’s needs and criteria.
In summary, the RFQ process begins with document preparation, moves on to vendor list definition, and involves issuing the RFQ and receiving offers. The final steps include reviewing the offers and ultimately awarding the contract to the chosen supplier. This systematic process ensures that the buyer can gather necessary information, evaluate different options, and make an informed decision when selecting a supplier for their project or procurement needs.
What is the difference between RFQ and RFP in procurement?
The main difference between RFQ and RFP in procurement lies in their objectives and scope. RFQ focuses on obtaining price quotes for specific commodities or materials, while RFP seeks comprehensive proposals that address the buyer’s problem or need. RFQ is more suitable for procurement of goods, while RFP is commonly used for services or complex projects. RFP involves evaluating multiple criteria beyond pricing, such as technical skills, experience, and legal compliance, while RFQ primarily revolves around pricing considerations.
Conclusion
The Request for Quotation is a valuable tool for buyers to acquire materials at competitive prices. In government and public sectors, utilizing an RFQ is obligatory to ensure equal opportunities for all sellers.
